- Phantom of the Flopera (YouTube) — Bach’s Tocata and Fugue in D Minor (BWV 565) as performed by floppy drives. Creative intimacy with one’s tools is a sign of mastery. (via Andy Baio)
- Save Entire BBC Archive (Ben Goldacre) — I pointed earlier to the questionable BBC closure of scores of websites in the name of cost-cutting. It’s a torrent of an archive of spidered BBC websites. (via Andy Baio)
- Android Hidden NFC Capabilities Unlocked — Gibraltar Software Factory, based in Argentina, went through the source code of Android 2.3 and found that Google has purposefully hidden several NFC related API calls, most likely due to the fact that they’re not quite stable enough for public release. Some minor tweaking of the source code, and boom, they’ve enabled write support for NFC tags. This means mobile phones will not just read RFID tags, but also act like RFID tags. (via Chris Heathcote on Delicious)
- Pinboard Creator Maciej Ceglowski (ReadWriteWeb) — I think many developers (myself included) are easily seduced by new technology and are willing to burn a lot of time rigging it together just for the joy of tinkering. So nowadays we see a lot of fairly uninteresting web apps with very technically sweet implementations. In designing Pinboard, I tried to steer clear of this temptation by picking very familiar, vanilla tools wherever possible so I would have no excuse for architectural wank. The other reason I like the approach is that the tried-and-true stuff is extensively debugged and documented. The chances of you finding a bug in MySQL or PHP as the author of a mid-sized website are microscopic. That’s not the case for newer infrastructure like NoSQL or the various web frameworks.
"LAMP" entries

Full-stack tensions on the Web
How much do you need to know?
 I expected that CSSDevConf would be primarily a show about front-end work, focused on work in clients and specifically in browsers. I kept running into conversations, though, about the challenges of moving between the front and back end, the client and the server side. Some were from developers suddenly told that they had to become “full-stack developers” covering the whole spectrum, while others were from front-end engineers suddenly finding a flood of back-end developers tinkering with the client side of their applications. “Full-stack” isn’t always a cheerful story.
I expected that CSSDevConf would be primarily a show about front-end work, focused on work in clients and specifically in browsers. I kept running into conversations, though, about the challenges of moving between the front and back end, the client and the server side. Some were from developers suddenly told that they had to become “full-stack developers” covering the whole spectrum, while others were from front-end engineers suddenly finding a flood of back-end developers tinkering with the client side of their applications. “Full-stack” isn’t always a cheerful story.
In the early days of the Web, “full-stack” was normal. While there were certainly people who focused on running web servers or designing sites as beautiful as the technology would allow, there were lots of webmasters who knew how to design a site, write HTML, manage a server, and maybe write some CGI code for early applications.
Formal separation of concerns among HTML, CSS, and JavaScript made it easier to share responsibilities among specialists. As the dot-com boom proceeded, specialization accelerated, with dedicated designers, programmers, and sysadmins coming to the work. Perhaps there were too many titles.
Even as the bust set in, specialization remained the trend because Web projects — especially on the server side — had grown far more complicated. They weren’t just a server and a few scripts, but a complete stack, including templates, logic, and usually a database. Whether you preferred the LAMP stack, a Microsoft ASP stack, or perhaps Java servlets and JSP, the server side rapidly became its own complex arena. Intranet development in particular exploded as a way to build server-based applications that could (cheaply) connect data sources to users on multiple platforms. Writing web apps was faster and cheaper than writing desktop apps, with more tolerance for platform variation.
Read more…

Introducing “A Field Guide to the Distributed Development Stack”
Tools to develop massively distributed applications.
Editor’s Note: At the Velocity Conference in Barcelona we launched “A Field Guide to the Distributed Development Stack.” Early response has been encouraging, with reactions ranging from “If I only had this two years ago” to “I want to give a copy of this to everyone on my team.” Below, Andrew Odewahn explains how the Guide came to be and where it goes from here.
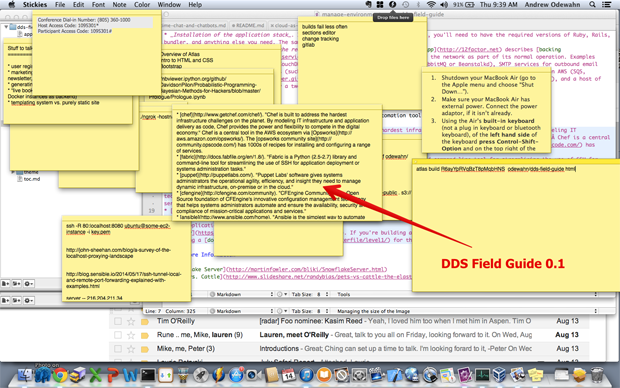
As we developed Atlas, O’Reilly’s next-generation publishing tool, it seemed like every day we were finding interesting new tools in the DevOps space, so I started a “Sticky” for the most interesting-looking tools to explore.
At first, this worked fine. I was content to simply keep a list, where my only ordering criteria was “Huh, that looks cool. Someday when I have time, I’ll take a look at that,” in the same way you might buy an exercise DVD and then only occasionally pull it out and think “Huh, someday I’ll get to that.” But, as anyone who has watched DevOps for any length of time can tell you, it’s a space bursting with interesting and exciting new tools, so my list and guilt quickly got out of hand.